astro.wikisort.org - Asteroid
Aethra (minor planet designation: 132 Aethra) is a metallic asteroid and Mars-crosser on an eccentric orbit from the asteroid belt. It measures approximately 40 kilometers in diameter.
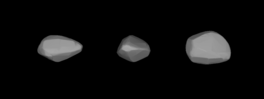 Lightcurve-based 3D-model of Aethra | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | James C. Watson |
| Discovery date | 13 June 1873 |
| Designations | |
MPC designation | (132) Aethra |
| Pronunciation | /ˈiːθrə/[1] |
Named after | Aethra |
Alternative designations | A873 LA; 1922 XB; 1949 MD; 1953 LF |
Minor planet category | Mars crosser |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 31 July 2016 (JD 2457600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 142.50 yr (52049 d) |
| Aphelion | 3.6250 AU (542.29 Gm) |
| Perihelion | 1.5895 AU (237.79 Gm) |
Semi-major axis | 2.6073 AU (390.05 Gm) |
| Eccentricity | 0.39036 |
Orbital period (sidereal) | 4.21 yr (1537.7 d) |
Average orbital speed | 17.72 km/s |
Mean anomaly | 38.271° |
Mean motion | 0° 14m 2.796s / day |
| Inclination | 24.997° |
Longitude of ascending node | 258.408° |
Argument of perihelion | 255.216° |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 35.83±6.59 km[3] 42.87±1.6 km[2] |
| Mass | (0.41±2.71)×1018 kg[3] |
Synodic rotation period | 5.1684 h (0.21535 d)[2] |
Geometric albedo | 0.1990±0.015[2] |
Spectral type | M |
Absolute magnitude (H) | 9.38[2] |
It was discovered by James Craig Watson in 1873 and is the first such Mars-crosser asteroid to be identified. As a Mars-crosser asteroid, Aethra is the lowest numbered asteroid to not have proper orbital elements due to recurring perturbations by Mars. It has a rather eccentric orbit that sometimes brings it closer to the Sun than the planet Mars.
With an original observation arc of only 22 days, 132 Aethra was a lost asteroid between 1873 and 1922.[4][5]
The varying light curve of the asteroid implies an elongated or irregular shape for its body.
It is named after Aethra, the mother of Theseus in Greek mythology.
References
- Noah Webster (1884) A Practical Dictionary of the English Language
- "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 132 Aethra" (2000-06-10 last obs). Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- Carry, B. (December 2012). "Density of asteroids". Planetary and Space Science. 73 (1): 98–118. arXiv:1203.4336. Bibcode:2012P&SS...73...98C. doi:10.1016/j.pss.2012.03.009. See Table 1.
- Herget, Paul (1938). "The orbit and perturbations of (132) Aethra". Astronomical Journal. 47 (1081): 17–23. Bibcode:1938AJ.....47...17H. doi:10.1086/105455.
- Fred William Price (2000). The Planet Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. p. 192. ISBN 978-0-521-78981-3.
External links
- 132 Aethra at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 132 Aethra at the JPL Small-Body Database
На других языках
[de] (132) Aethra
(132) Aethra ist ein Asteroid des Asteroiden-Hauptgürtels, der am 13. Juni 1873 von James Craig Watson entdeckt wurde.- [en] 132 Aethra
[es] (132) Aethra
(132) Aethra es un asteroide perteneciente al grupo de los asteroides que cruzan la órbita de Marte descubierto el 13 de junio de 1873 por James Craig Watson desde el observatorio Detroit de Ann Arbor, Estados Unidos. Está nombrado por Etra, un personaje de la mitología griega.[2][ru] (132) Эфра
(132) Эфра (лат. Aethra) — астероид, относящийся к группе астероидов пересекающих орбиту Марса, принадлежащий к спектральному классу M. Он был обнаружен 13 июня 1873 года американским астрономом Дж. К. Уотсоном в Энн-Арбор, США и назван в честь Эфры, матери Тесея согласно греческой мифологии[1].Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии