astro.wikisort.org - Asteroid
1494 Savo, provisional designation 1938 SJ, is a stony background asteroid from the inner region of the asteroid belt, approximately 8 kilometers in diameter. Discovered by astronomer Yrjö Väisälä at the Turku Observatory in 1938, the asteroid was later named after the Finnish region of Savonia.[2]
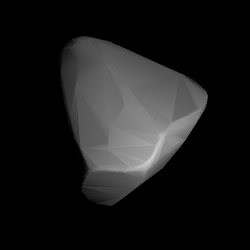 Shape of Savo modelled from its lightcurve | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Y. Väisälä |
| Discovery site | Turku Obs. |
| Discovery date | 16 September 1938 |
| Designations | |
MPC designation | (1494) Savo |
Named after | Savonia[2] (Finnish region) |
Alternative designations | 1938 SJ · 1925 RL 1938 SG1 · 1948 VR 1951 SV · 1953 GD 1966 HB · 1976 HZ |
Minor planet category | main-belt · (inner)[3] background[4] |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 4 September 2017 (JD 2458000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 78.50 yr (28,673 days) |
| Aphelion | 2.4777 AU |
| Perihelion | 1.9019 AU |
Semi-major axis | 2.1898 AU |
| Eccentricity | 0.1315 |
Orbital period (sidereal) | 3.24 yr (1,184 days) |
Mean anomaly | 114.29° |
Mean motion | 0° 18m 14.76s / day |
| Inclination | 2.4560° |
Longitude of ascending node | 195.02° |
Argument of perihelion | 184.32° |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 7.80±0.22 km[5] 7.804±0.219 km[5] 9.23±0.43 km[6] 10.30 km (calculated)[3] |
Synodic rotation period | 5.35011±0.00028 h[lower-alpha 1] 5.35020±0.00005 h[7] 5.35031±0.00005 h[7] 5.35059±0.00001 h[8] 5.35059±0.00005 h[9] 5.35062±0.00005 h[7] |
Geometric albedo | 0.173±0.017[6] 0.20 (assumed)[3] 0.349±0.061[5] |
Spectral type | SMASS = Sa[1] · S[3] |
Absolute magnitude (H) | 12.08±0.24[10] · 12.30[1][3][5] · 12.70[6] |
Discovery
Savo was discovered on 16 September 1938, by Finnish astronomer Yrjö Väisälä at the Iso-Heikkilä Observatory near Turku, Finland.[11] Two nights later, it was independently discovered by German astronomer Arno Arthur Wachmann at the Bergedorf Observatory in Hamburg.[2] However, the Minor Planet Center only acknowledges the first discoverer. The asteroid was first identified as 1925 RL at the Crimean Simeiz Observatory in September 1929, or nine years before its official discovery observation.[11]
Orbit and classification
Savo is an asteroid of the main belt's background population that does not belong to any known asteroid family.[4] It orbits the Sun in the inner asteroid belt at a distance of 1.9–2.5 AU once every 3 years and 3 months (1,184 days). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.13 and an inclination of 2° with respect to the ecliptic.[1] The body's observation arc begins with its official discovery observation at Turku in September 1938.[11]
Physical characteristics
In the SMASS classification, Savo is an Sa-subtype that transitions from the stony S-type to the A-type asteroids.[1]
Rotation period
In August 2006, a rotational lightcurve of Savo was obtained from photometric observations by Czech astronomer Petr Pravec at Ondřejov Observatory. Lightcurve analysis gave a well-defined rotation period of 5.35011 hours with a brightness amplitude of 0.52 magnitude (U=3), indicative for a non-spherical shape.[lower-alpha 1] Follow up observations at the Calvin College Observatory (H62) in 2007 and 2008, gave three nearly identical periods of 5.35020, 5.35031 and 5.35062 hours with an amplitude between 0.44 and 0.63 (U=3/3/3-).[7]
Poles
The asteroid's lightcurve has also been modeled twice. In 2011, the first modelling used photometric data from the AstDyS database and the Uppsala Asteroid Photometric Catalogue, and found two spin axis of (248.0°, −68.0°) and (83.0°, −66.0°) in ecliptic coordinates (λ, β).[9] A refined modeling in 2016, using the Lowell Photometric Database gave two poles of (50.0°, −65.0°) and (233.0°, −68.0°) in ecliptic coordinates.[8] Also, both studies found a concurring period of 5.35059 hours.[9][8]
Diameter and albedo
According to the surveys carried out by the Japanese Akari satellite and the NEOWISE mission of NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, Savo measures between 7.80 and 9.23 kilometers in diameter and its surface has an albedo between 0.173 and 0.349.[5][6] The Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link assumes a standard albedo for stony asteroids of 0.20 and calculates a diameter of 10.30 kilometers based on an absolute magnitude of 12.3.[3]
Naming
This minor planet was named after Finnish historical province of Savonia.[2] The official naming citation was published by the Minor Planet Center in January 1956 (M.P.C. 1350).[12]
Notes
- Pravec (2006) web: Lightcurve plot of (1494) Savo with a rotation period 5.35011±0.00028 hours with a brightness amplitude of 0.52 mag. Quality Code of 3. Summary figures for (1494) Savo at LCDB and data sheet at Ondrejov Asteroid Photometry Project
References
- "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 1494 Savo (1938 SJ)" (2017-03-29 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- Schmadel, Lutz D. (2007). "(1494) Savo". Dictionary of Minor Planet Names – (1494) Savo. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 119. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-29925-7_1495. ISBN 978-3-540-00238-3.
- "LCDB Data for (1494) Savo". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- "Asteroid 1494 Savo – Proper Elements". AstDyS-2, Asteroids – Dynamic Site. Retrieved 29 October 2019.
- Masiero, Joseph R.; Mainzer, A. K.; Grav, T.; Bauer, J. M.; Cutri, R. M.; Nugent, C.; et al. (November 2012). "Preliminary Analysis of WISE/NEOWISE 3-Band Cryogenic and Post-cryogenic Observations of Main Belt Asteroids". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 759 (1): 5. arXiv:1209.5794. Bibcode:2012ApJ...759L...8M. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/759/1/L8. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- Usui, Fumihiko; Kuroda, Daisuke; Müller, Thomas G.; Hasegawa, Sunao; Ishiguro, Masateru; Ootsubo, Takafumi; et al. (October 2011). "Asteroid Catalog Using Akari: AKARI/IRC Mid-Infrared Asteroid Survey". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. 63 (5): 1117–1138. Bibcode:2011PASJ...63.1117U. doi:10.1093/pasj/63.5.1117. (online, AcuA catalog p. 153)
- Dykhuis, Melissa J.; Molnar, Lawrence A.; Gates, Christopher J.; Gonzales, Joshua A.; Huffman, Jared J.; Maat, Aaron R.; et al. (March 2016). "Efficient spin sense determination of Flora-region asteroids via the epoch method". Icarus. 267: 174–203. Bibcode:2016Icar..267..174D. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2015.12.021. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- Durech, J.; Hanus, J.; Oszkiewicz, D.; Vanco, R. (March 2016). "Asteroid models from the Lowell photometric database". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 587: 6. arXiv:1601.02909. Bibcode:2016A&A...587A..48D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201527573.
- Hanus, J.; Durech, J.; Broz, M.; Warner, B. D.; Pilcher, F.; Stephens, R.; et al. (June 2011). "A study of asteroid pole-latitude distribution based on an extended set of shape models derived by the lightcurve inversion method". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 530: 16. arXiv:1104.4114. Bibcode:2011A&A...530A.134H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201116738.
- Veres, Peter; Jedicke, Robert; Fitzsimmons, Alan; Denneau, Larry; Granvik, Mikael; Bolin, Bryce; et al. (November 2015). "Absolute magnitudes and slope parameters for 250,000 asteroids observed by Pan-STARRS PS1 - Preliminary results". Icarus. 261: 34–47. arXiv:1506.00762. Bibcode:2015Icar..261...34V. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2015.08.007. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- "1494 Savo (1938 SJ)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- Schmadel, Lutz D. "Appendix – Publication Dates of the MPCs". Dictionary of Minor Planet Names – Addendum to Fifth Edition (2006–2008). Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 221. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-01965-4. ISBN 978-3-642-01964-7.
External links
- Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB), query form (info Archived 16 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine)
- Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, Google books
- Asteroids and comets rotation curves, CdR – Observatoire de Genève, Raoul Behrend
- Discovery Circumstances: Numbered Minor Planets (1)-(5000) – Minor Planet Center
- 1494 Savo at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 1494 Savo at the JPL Small-Body Database
На других языках
[de] (1494) Savo
(1494) Savo ist ein Asteroid des Hauptgürtels, der am 16. September 1938 von dem finnischen Astronomen Yrjö Väisälä in Turku entdeckt wurde.- [en] 1494 Savo
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии