astro.wikisort.org - Pianeta
HR 8799 b è un pianeta extrasolare che orbita attorno alla stella bianca di sequenza principale HR 8799, situata nella costellazione di Pegaso a 129 anni luce dal sistema solare. È il pianeta più esterno del sistema planetario.
| HR 8799 b | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Stella madre | HR 8799 |
| Scoperta | 13 novembre 2008 |
| Scopritori | Marois et al, Telescopio Keck - Gemini Nord |
| Classificazione | Gigante gassoso o sub-nana bruna |
| Distanza dal Sole | 129 ± 4 a.l.[1][2] |
| Coordinate | |
| (all'epoca J2000.0) | |
| Ascensione retta | 23h 07m 28,7150s[3] |
| Declinazione | +21° 08′ 03,302″[3] |
| Parametri orbitali | |
| Semiasse maggiore | ~ 10000000000 km ~ 68 UA[4][5] |
| Periodo orbitale | ~ 460 anni[4][5] |
| Eccentricità | sconosciuta[6] |
| Dati fisici | |
| Diametro medio | 1,2 ± 0,1 RJ[4] |
| Massa | 7+4
−2 MJ[7] |
| Temperatura superficiale | 870 ± 50 K[4] (media) |
Caratteristiche

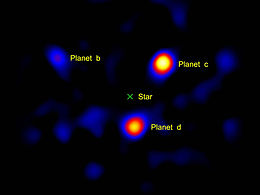
La massa del pianeta è compresa tra le 4 e le 10 volte quella di Giove,[4] con un raggio dal 10 al 30% superiore[4] rispetto a quello del gigante del sistema solare. Il pianeta orbita ad una distanza media dalla stella madre di circa 68 UA (a 7 UA dal bordo più interno della cintura asteroidale), con un'eccentricità orbitale ancora sconosciuta ed un periodo stimato in 460 anni.[4]
Assieme agli altri due pianeti del sistema, c e d, HR 8799 b è stato scoperto il 13 novembre 2008 tramite i telescopi Keck e Gemini Nord, nelle Hawaii, che hanno consentito l'osservazione diretta dei corpi celesti.[4][8][9][10]

Nel 2009 si è tuttavia scoperto che il telescopio spaziale Hubble aveva già ripreso HR 8799 b undici anni prima, nel 1998, suggerendo dunque che numerosi altri esopianeti potrebbero essere individuati semplicemente analizzando gli archivi fotografici del telescopio.[11]
Note
- F. van Leeuwen, HIP 114189, su webviz.u-strasbg.fr, Hipparcos, the New Reduction, 2007. URL consultato il 13-11-2008.
- Calcolata a partire dalla parallasse:
- V* V342 Peg -- Variable Star of gamma Dor type, su simbad.u-strasbg.fr, SIMBAD. URL consultato il 20-12-2008..
- Christian Marois, et al., Direct Imaging of Multiple Planets Orbiting the Star HR 8799, in Science, vol. 322, n. 5906, novembre 2008, pp. 1348–1352, DOI:10.1126/science.1166585. URL consultato il 20 dicembre 2008 (archiviato dall'url originale il 2 giugno 2016).
- Valori ottenuti considerando il piano dell'orbita circolare e visto frontalmente.
- Fabrycky et al, Stability of the directly imaged multiplanet system HR 8799: resonance and masses, su arxiv.org, 1º dicembre 2008. URL consultato il 2-12-2008.
- Planet HR 8799 b, in Enciclopedia dei pianeti extrasolari.
- Astronomers capture first images of newly-discovered solar system, su keckobservatory.org, W. M. Keck Observatory, 13 novembre 2008. URL consultato il 2-12-2008 (archiviato dall'url originale il 26 novembre 2013).
- Gemini Releases Historic Discovery Image of Planetary First Family, su gemini.edu, Gemini Observatory, 13 novembre 2008. URL consultato il 2-12-2008.
- Joel Achenbach, Scientists Publish First Direct Images of Extrasolar Planets, The Washington Post, 13 novembre 2008. URL consultato il 2-12-2008.
- Lafrenière et al., HST/NICMOS detection of HR 8799 b in 1998, su arxiv.org, 18 febbraio 2009. URL consultato il 1-04-2009.
Voci correlate
Altri progetti
 Wikimedia Commons contiene immagini o altri file su HR 8799 b
Wikimedia Commons contiene immagini o altri file su HR 8799 b
Collegamenti esterni
- HR 8799 d, su media4.obspm.fr, Exoplanets. URL consultato il 20 dicembre 2008 (archiviato dall'url originale il 4 marzo 2012).
На других языках
[en] HR 8799 b
HR 8799 b is an extrasolar planet located approximately 129 light-years away in the constellation of Pegasus, orbiting the 6th magnitude Lambda Boötis star HR 8799. It has a mass between 4 and 7 [2]Jupiter masses and a radius from 10 to 30% larger than Jupiter's. It orbits at 68 AU from HR 8799 (or 7 AU inside the inner edge of the dust disk orbiting the star) with an unknown eccentricity and a period of 460 years, and is the outermost known planet in the HR 8799 system. Along with two other planets orbiting HR 8799, the planet was discovered on November 13, 2008 by Marois et al., using the Keck and Gemini observatories in Hawaii. These planets were discovered using the direct imaging technique.[1][3][4][5][6][es] HR 8799 b
HR 8799 b es un planeta extrasolar que se encuentra a aproximadamente 129 años luz en la constelación de Pegaso orbitando la estrella Lambda Bootis HR 8799. Su masa es entre 5 y 11 veces la masa de Júpiter y su radio es entre un 10 % y un 30 % mayor que el de Júpiter. El planeta orbita a una distancia media de 68 UA (7 UA desde el borde interior del disco circunestelar que rodea la estrella) de su estrella, su excentricidad se desconoce y su periodo orbital es de 460 años. Es el planeta más alejado conocido del sistema de HR 8799. Junto con otros dos planetas que orbitan HR 8799, este planeta fue descubierto el 13 de noviembre de 2008 por Marois et al., usando el Telescopio Keck y el observatorio Gemini en Hawái. Estos planetas fueron descubiertos usando la técnica de imagen directa.[6][7][8][9][10]- [it] HR 8799 b
[ru] HR 8799 b
HR 8799 b — газовый гигант из планетной системы HR 8799. Находится в созвездии Пегаса на расстоянии 129 световых лет от Земли. Открыт методом прямого наблюдения обсерваториями Кека и Джемини в 2008 году.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
