astro.wikisort.org - Asteroid
(419624) 2010 SO16 is a sub-kilometer asteroid in a co-orbital configuration with Earth, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It was discovered by the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer space telescope (WISE) on 17 September 2010.[1][2]
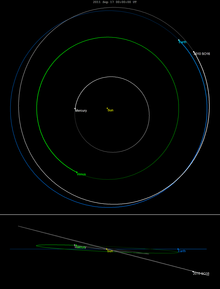 Orbit with inner solar system | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | WISE |
| Discovery site | Low Earth orbit |
| Discovery date | 17 September 2010 |
| Designations | |
MPC designation | (419624) 2010 SO16 |
Alternative designations | 2010 SO16 |
Minor planet category | Apollo · NEO · PHA[1][2] |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 4 September 2017 (JD 2458000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 5.28 yr (1,928 days) |
| Aphelion | 1.0785 AU |
| Perihelion | 0.9272 AU |
Semi-major axis | 1.0028 AU |
| Eccentricity | 0.0754 |
Orbital period (sidereal) | 1.00 yr (367 days) |
Mean anomaly | 173.30° |
Mean motion | 0° 58m 53.04s / day |
| Inclination | 14.520° |
Longitude of ascending node | 40.397° |
Argument of perihelion | 108.99° |
| Earth MOID | 0.0299 AU (11.6 LD) |
| Physical characteristics | |
Mean diameter | 0.357±0.126 km[3] |
Geometric albedo | 0.084±0.057[4] |
Absolute magnitude (H) | 20.5[1] |
Description
The orbit was described by Apostolos Christou and David Asher at the Armagh Observatory in Northern Ireland.[5] The object has an absolute magnitude of 20.5.[1] Observations by the discovering WISE telescope give a diameter of 357 meters and an albedo of 0.084.[3][4]
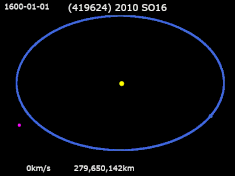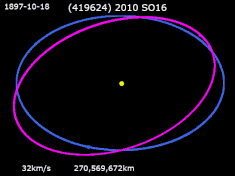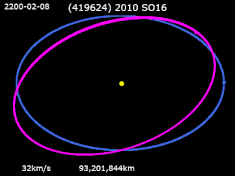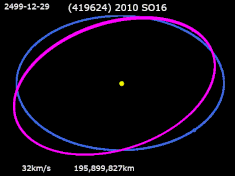
2010 SO16 has a horseshoe orbit that allows it to stably share Earth's orbital neighborhood without colliding with it. It is one of a handful of known asteroids with an Earth-following orbit, a group that includes 3753 Cruithne, and the only known asteroid in an horseshoe orbit with Earth. It is, however, neither an Aten asteroid nor an Apollo asteroid because the semi-major axis of its orbit is neither less than nor greater than 1 AU, but oscillates between approximately 0.996 and 1.004 AU, with a period of about 350 years.[5] In its ~350 yr horseshoe cycle, it never approaches Earth more closely than about 0.15 AU, alternately trailing and leading.
According to various simulations 2010 SO16 will remain in this orbit for at least 120,000 years and possibly for more than a million years, which is unusually stable compared to other similar objects.[6] One reason for this stability is its low orbital eccentricity, .[5]
A precovery of 2010 SO16 may have been located in a 2005 Spitzer Space Telescope image.[7]



See also
- 3753 Cruithne – a horseshoe companion of the Earth
- 2006 RH120 – a small asteroid that sometimes temporarily gets caught in Earth orbit
- 2002 AA29 – a horseshoe companion of the Earth
- Natural satellite
- 2001 GO2
- 2002 AA29
- 2003 YN107
- 2006 JY26
- 2012 FC71
- Orbital resonance
References
- "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 419624 (2010 SO16)" (2015-12-28 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- "419624 (2010 SO16)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- Nugent, C. R.; Mainzer, A.; Masiero, J.; Bauer, J.; Cutri, R. M.; Grav, T.; et al. (December 2015). "NEOWISE Reactivation Mission Year One: Preliminary Asteroid Diameters and Albedos". The Astrophysical Journal. 814 (2): 13. arXiv:1509.02522. Bibcode:2015ApJ...814..117N. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/814/2/117.
- Mainzer, A.; Grav, T.; Masiero, J.; Bauer, J.; Cutri, R. M.; McMillan, R. S.; et al. (November 2012). "Physical Parameters of Asteroids Estimated from the WISE 3-Band Data and NEOWISE Post-Cryogenic Survey". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 760 (1): 6. arXiv:1210.0502. Bibcode:2012ApJ...760L..12M. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/760/1/L12.
- Christou, A. A.; Asher, D. J. (July 2011). "A long-lived horseshoe companion to the Earth". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 414 (4): 2965–2969. arXiv:1104.0036. Bibcode:2011MNRAS.414.2965C. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.18595.x.
- Asteroid Discovered in Horseshoe-Shaped Orbit, The Physics arXiv Blog, Technology Review, 4/05/2011
- "New Tool Finds Buried Treasure in Spitzer Archives". NASA/JPL. 3 April 2014. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
External links
- (419624) 2010 SO16 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- (419624) 2010 SO16 at ESA–space situational awareness
- (419624) 2010 SO16 at the JPL Small-Body Database
На других языках
[de] (419624) 2010 SO16
(419624) 2010 SO16 ist ein Asteroid vom Apollo-Typ, der 2010 mithilfe des Weltraumteleskops WISE entdeckt wurde.[1][2] Seine Bahnneigung beträgt 14,5°, die absolute Helligkeit 20,6.[3] Mit einem Durchmesser von ca. 300 Metern ist er der bisher größte bekannte Asteroid, der auf einer erdgebundenen Hufeisenumlaufbahn läuft, und insgesamt das vierteAnm1 bisher entdeckte Objekt dieser Art.- [en] (419624) 2010 SO16
[ru] (419624) 2010 SO16
(419624) 2010 SO16 — маленький околоземный астероид из группы аполлона, обладающий крайне интересной орбитой: очень близкой к орбите Земли, но не допускающей приближений астероида к нашей планете менее, чем на 0,15 а.е. Астероид был открыт 17 сентября 2010 года с помощью инфракрасного космического телескопа WISE, данные с которого были проанализированы в обсерватории Армы, близ одноимённого города в Ирландии[1]. Абсолютная звёздная величина этого астероида составляла всего 20,7m. Таким образом, для его наблюдения требуются очень крупные телескопы. При неизвестном альбедо поверхности, это позволяет оценить размер астероида в 200–400 метров.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
