astro.wikisort.org - Science
The Cosmic Calendar is a method to visualize the chronology of the universe, scaling its currently understood age of 13.8 billion years to a single year in order to help intuit it for pedagogical purposes in science education or popular science.
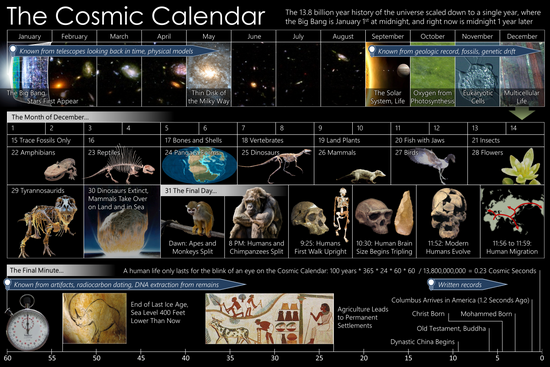
In this visualization, the Big Bang took place at the beginning of January 1 at midnight, and the current moment maps onto the end of December 31 just before midnight.[1] At this scale, there are 437.5 years per cosmic second, 1.575 million years per cosmic hour, and 37.8 million years per cosmic day.
The concept was popularized by Carl Sagan in his 1977 book The Dragons of Eden and on his 1980 television series Cosmos.[2] Sagan goes on to extend the comparison in terms of surface area, explaining that if the Cosmic Calendar is scaled to the size of a football field, then "all of human history would occupy an area the size of [his] hand".[3]
A similar analogy used to visualize the geologic time scale and the history of life on Earth is the Geologic Calendar
Cosmology
| Date | Gya (billion years ago) | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Jan | 13.8 | Big Bang, as seen through cosmic background radiation, which would have been last emitted 14 minutes after midnight |
| 19 Jan | 13.1 | Oldest known Gamma Ray Burst |
| 26 Jan | 12.85 | First galaxies form[4] |
| 16 Mar | 11 | Milky Way Galaxy formed |
| 13 May | 8.8 | Milky Way Galaxy disk formed |
| 2 Sep | 4.57 | Formation of the Solar System |
| 6 Sep | 4.4 | Oldest rocks known on Earth |
Date in year calculated from formula
T(days) = 365 days * ( 1- T_Gya/13.797 )
Evolution of life on Earth
| Date | Gya (billion years ago) | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 14 Sep | 4.1 | First known remains of biotic life (discovered in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia).[5][6] |
| 21 Sep | 3.8 | First Life (Prokaryotes)[7][8][9] |
| 30 Sep | 3.4 | Photosynthesis |
| 29 Oct | 2.4 | Oxygenation of atmosphere |
| 9 Nov | 2 | Complex cells (Eukaryotes) |
| 5 Dec | 0.8 | First multicellular life[10] |
| 7 Dec | 0.67 | Simple animals |
| 14 Dec | 0.55 | Arthropods (ancestors of insects, arachnids) |
| 17 Dec | 0.5 | Fish and Proto-amphibians |
| 20 Dec | 0.45 | Land plants; Ordovician–Silurian extinction events |
| 21 Dec | 0.4 | Insects and seeds |
| 22 Dec | 0.36 | Amphibians; Late Devonian extinction |
| 23 Dec | 0.3 | Reptiles |
| 24 Dec | 0.25 | Permian–Triassic extinction event; 57% of all biological families and 83% of all genera die |
| 25 Dec | 0.23 | Dinosaurs |
| 26 Dec | 0.2 | Mammals; Triassic–Jurassic extinction event |
| 27 Dec | 0.15 | Birds (avian dinosaurs) |
| 28 Dec | 0.13 | Flowers |
| 30 Dec, 06:24 | 0.065 | Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, non-avian dinosaurs die out[11] |
Human evolution
This section does not cite any sources. (January 2021) |
| Date / time | Mya (million years ago) | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 30 Dec | 65 | Primates |
| 31 Dec, 06:05 | 15 | Apes |
| 31 Dec, 14:24 | 12.3 | Hominids |
| 31 Dec, 22:24 | 2.5 | Primitive humans and stone tools |
| 31 Dec, 23:44 | 0.4 | Domestication of fire |
| 31 Dec, 23:52 | 0.2 | Anatomically modern humans |
| 31 Dec, 23:55 | 0.11 | Beginning of most recent Glacial Period |
| 31 Dec, 23:58 | 0.035 | Sculpture and painting |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:32 | 0.012 | Agriculture |
History begins
This section does not cite any sources. (January 2021) |
| Date / time | kya (thousand years ago) | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 31 Dec, 23:59:33 | 12.0 | End of the last Ice Age |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:41 | 8.3 | Flooding of Doggerland |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:46 | 6.0 | Chalcolithic |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:47 | 5.5 | Early Bronze Age; Proto-writing; Building of Stonehenge Cursus |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:48 | 5.0 | First Dynasty of Egypt, Early Dynastic period in Sumer, beginning of Indus Valley civilisation |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:49 | 4.5 | Alphabet, Akkadian Empire, wheel |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:51 | 4.0 | Code of Hammurabi, Middle Kingdom of Egypt |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:52 | 3.5 | Late Bronze Age to early Iron Age; Minoan eruption |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:53 | 3.0 | Iron Age; beginning of classical antiquity |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:54 | 2.5 | Buddha, Mahavira, Zoroaster, Confucius, Achaemenid Empire, Qin Dynasty, Classical Greece, Ashokan Empire, Vedas Completed, Euclidean geometry, Archimedean Physics, Roman Republic |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:55 | 2.0 | Ptolemaic astronomy, Roman Empire, Christ, invention of numeral 0, Gupta Empire |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:56 | 1.5 | Muhammad, Maya civilization, Song Dynasty, rise of Byzantine Empire |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:58 | 1.0 | Mongol Empire, Maratha Empire, Crusades, Christopher Columbus voyages to the Americas, Renaissance in Europe, Classical music to the time of Johann Sebastian Bach |
| 31 Dec, 23:59:59 | 0.5 | Modern History; the last 437.5 years before present. |
See also
- Geologic Calendar
- Big History – Academic discipline which examines history from the Big Bang to the present
- Detailed logarithmic timeline – Timeline of the history of the universe, Earth, and mankind
- List of timelines
- Timeline of ancient history
- Timeline of early modern history
- Timeline of the evolutionary history of life – Major events during the development of life
- Timeline of the far future – Scientific projections regarding the far future
- Timeline of human evolution – Chronological outline of major events in the development of the human species
- Timeline of human prehistory
- Timelines of modern history
- Timeline of natural history
- Timeline of plant evolution – Chronological outline of major events in the development of plants
- Chronology of the universe – History and future of the universe
- Timeline of the Middle Ages – Timeline
- Cosmic time
- History of Earth – Development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day
References
- Therese Puyau Blanchard (1995). "The Universe At Your Fingertips Activity: Cosmic Calendar". Astronomical Society of the Pacific. Archived from the original on 2007-12-16. Retrieved 2007-12-15.
- Cosmos, episode 1 (1980)
- Episode 1: The Shores of the Cosmic Ocean (Cosmos: A Personal Voyage, Carl Sagan)
- "First Galaxies Born Sooner After Big Bang Than Thought". Space.com. Retrieved 2015-11-07.
- Borenstein, Seth (19 October 2015). "Hints of life on what was thought to be desolate early Earth". Excite. Yonkers, NY: Mindspark Interactive Network. Associated Press. Retrieved 2015-10-20.
- Bell, Elizabeth A.; Boehnike, Patrick; Harrison, T. Mark; et al. (19 October 2015). "Potentially biogenic carbon preserved in a 4.1 billion-year-old zircon" (PDF). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112 (47): 14518–21. Bibcode:2015PNAS..11214518B. doi:10.1073/pnas.1517557112. ISSN 1091-6490. PMC 4664351. PMID 26483481. Retrieved 2015-10-20. Early edition, published online before print.
- Yoko Ohtomo; Takeshi Kakegawa; Akizumi Ishida; Toshiro Nagase; Minik T. Rosing (8 December 2013). "Evidence for biogenic graphite in early Archaean Isua metasedimentary rocks". Nature Geoscience. 7: 25–28. Bibcode:2014NatGe...7...25O. doi:10.1038/ngeo2025.
- Borenstein, Seth (13 November 2013). "Oldest fossil found: Meet your microbial mom". AP News. Retrieved 15 November 2013.
- Noffke, Nora; Christian, Daniel; Wacey, David; Hazen, Robert M. (8 November 2013). "Microbially Induced Sedimentary Structures Recording an Ancient Ecosystem in the ca. 3.48 Billion-Year-Old Dresser Formation, Pilbara, Western Australia". Astrobiology. 13 (12): 1103–24. Bibcode:2013AsBio..13.1103N. doi:10.1089/ast.2013.1030. PMC 3870916. PMID 24205812.
- Erwin, Douglas H. (9 November 2015). "Early metazoan life: divergence, environment and ecology". Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 370 (20150036): 20150036. doi:10.1098/rstb.2015.0036. PMC 4650120. PMID 26554036.
- "Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey (@35min)". Archived from the original on 2014-03-11. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
External links
- More information on the image used for this article.
- The Cosmic Calendar in a Google Calendar format
- The Cosmic Calendar relayed in real time.
На других языках
- [en] Cosmic Calendar
[ru] Космический календарь
«Космический календарь» (англ. Cosmic Calendar) — метод визуализации обширной истории Вселенной, при котором 13,8 миллиардов лет сжимаются до одного календарного года.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
