astro.wikisort.org - Star
G117-B15A[5] is a small, well-observed variable white dwarf star of the DAV, or ZZ Ceti, type in the constellation of Leo Minor.
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Leo Minor |
| Right ascension | 09h 24m 16s[2] |
| Declination | +35° 16.9′[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 15.5[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | DAV4[2] |
| U−B color index | -0.6[2] |
| B−V color index | 0.2[2] |
| Variable type | DAV[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: -136[3] mas/yr Dec.: 22[3] mas/yr |
| Details | |
| Temperature | 12400[4] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
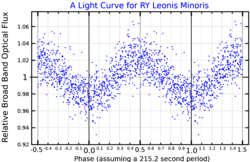
G117-B15A was found to be variable in 1974 by Richer and Ulrych,[6] and this was confirmed in 1976 by McGraw and Robinson.[7] In 1984 it was demonstrated that the star's variability is due to nonradial gravity wave pulsations. As a consequence, its timescale for period change is directly proportional to its cooling timescale, allowing its cooling rate to be measured using astroseismological techniques.[5] Its age is estimated at 400 million years.[8] Its light curve has a dominant period of 215.2 seconds,[5] which is estimated to increase by approximately one second each 14 million years.[9] G117-B15A has been claimed to be the most stable optical clock ever found, much more stable than the ticks of an atomic clock.[10] It is also the first pulsating white dwarf to have its main pulsation mode index identified.[5]
X-ray source
An X-ray source in the constellation Leo Minor is the white dwarf G117-B15A.[11]
Notes
- Chote, P.; Sullivan, D. J.; Brown, R.; Harrold, S. T.; Winget, D. E.; Chandler, D. W. (May 2014). "Puoko-nui: a flexible high-speed photometric system". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 440 (2): 1490–1497. doi:10.1093/mnras/stu348. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- A Catalog of Spectroscopically Identified White Dwarfs, George P. McCook and Edward M. Sion, Astrophysical Journal Supplement 121, #1 (March 1999), pp. 1–130. CDS ID III/210. Astrometric data updated to J2000.0.
- "V* RY LMi". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg.
- Kepler, S. O.; Winget, D. E.; Vanderbosch, Zachary P.; Castanheira, Barbara Garcia; Hermes, J. J.; Bell, Keaton J.; Mullally, Fergal; Romero, Alejandra D.; Montgomery, M. H.; Degennaro, Steven; Winget, Karen I.; Chandler, Dean; Jeffery, Elizabeth J.; Fritzen, Jamile K.; Williams, Kurtis A.; Chote, Paul; Zola, Staszek (2020). "The Pulsating White Dwarf G117-B15A: Still the Most Stable Optical Clock Known". The Astrophysical Journal. 906: 7. arXiv:2010.16062. Bibcode:2021ApJ...906....7K. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abc626. S2CID 226222216.
- Kepler, S. O.; et al. (2000-05-10). "Evolutionary Timescale of the Pulsating White Dwarf G117-B15A: The Most Stable Optical Clock Known". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 534 (2): L185–L188. arXiv:astro-ph/0003478. Bibcode:2000ApJ...534L.185K. doi:10.1086/312664. PMID 10813678. S2CID 14540467.
- High-frequency optical variables. II. Luminosity-variable white dwarfs and maximum entropy spectral analysis, H. B. Richer and T. J. Ulrych, Astrophysical Journal 192 (September 1974), pp. 719–730.
- High-speed photometry of luminosity-variable DA dwarfs: R808, GD 99, and G 117-B15A, J. T. McGraw and E. L. Robinson, Astrophysical Journal 205 (May 1976), pp. L155–L158.
- Pivetta, Marcos (January 2006). "The star of the moment". Retrieved 2007-06-06.
- From Ṗ=2.3·10−15 in Kepler et al.
- McDonald Observatory. "Astronomers Find Most Stable Optical Clock in Heavens; Aids Understanding of Stars' Lives". McDonald Observatory. Retrieved 2007-06-06.[permanent dead link]
- Kepler SO (December 5, 2005). "Astronomers Find Most Stable Optical Clock In Heavens".
See also
На других языках
- [en] G 117-B15A
[es] RY Leonis Minoris
RY Leonis Minoris (RY LMi / G 117-15A / WD 0921+354)[1] es una enana blanca situada en la constelación de Leo Minor a 150 años luz de distancia del Sistema Solar.[2] Con una edad estimada de 400 millones de años,[2] tiene una temperatura efectiva entre 11.600 y 12.400 K.[3]Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии