astro.wikisort.org - Star
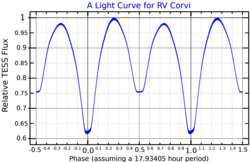
RV Corvi is an eclipsing binary star system in the southern constellation of Corvus. The brightness of the pair regularly ranges in apparent visual magnitude from 8.6 down to 9.16 over a period 18 hours,[4] even the brightest of which is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. The system is located at a distance of approximately 690 light-years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of ~19 km/s.[8]
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Corvus |
| Right ascension | 12h 37m 40.711s[2] |
| Declination | −19° 34′ 40.03″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.77[3] (8.6 - 9.16)[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Main sequence |
| Spectral type | F0V[5] (F0 + G0)[6] |
| B−V color index | 0.404±0.026[3] |
| Variable type | β Lyr[7] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 19.0±4.6[8] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −29.326 mas/yr[2] Dec.: 8.954 mas/yr[2] |
| Parallax (π) | 4.7351 ± 0.0812 mas[2] |
| Distance | 690 ± 10 ly (211 ± 4 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 2.32[3] |
| Orbit[9] | |
| Period (P) | 0.7473 d |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.00 |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2445792.3578 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 0.00° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 64 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 235 km/s |
| Details | |
| Primary | |
| Mass | 1.64±0.14[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 2.16 or 2.18 ± 0.08[9] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 8.4 or 8.5 ± 0.6[9] L☉ |
| Secondary | |
| Mass | 0.44±0.03[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.19 or 1.20 ±0.04[9] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.2 or 1.5 ± 0.1[9] L☉ |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
The variability of this system was discovered by H. H. Swope.[11] In 1942, Irene G. Buttery published an orbital period of 0.74728 days for the system, showing this is an eclipsing binary.[12] It is a near-contact binary with both stars showing the effect of tidal interactions and the facing sides are less than 10% of the orbital separation apart, but are not in contact.[13] One or both stars may show an excess of luminosity on their facing sides.[9] The system is composed of stars of spectral types F0 and G0, which orbit each other every 0.7473 days.[6]
References
- "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. S2CID 119257644.
- Watson, Christopher (4 January 2010). "RV Corvi". The International Variable Star Index. American Association of Variable Star Observers. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- Houk, Nancy; Smith-Moore, M. (1978). Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars. Vol. 4. Ann Arbor: Dept. of Astronomy, University of Michigan. Bibcode:1988mcts.book.....H.
- Malkov, O. Yu.; et al. (2006). "A catalogue of eclipsing variables". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 446 (2): 785–89. Bibcode:2006A&A...446..785M. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053137.
- Samus, N. N.; et al. (2017). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars". Astronomy Reports. 5.1. 61 (1): 80–88. Bibcode:2017ARep...61...80S. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. S2CID 125853869. Retrieved 2021-11-27.
- Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv:1606.08053. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. S2CID 119231169.
- McFarlane, T. M.; et al. (December 1986). "Contact and near-contact binary systems - V. RV Corvi". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 223 (3): 595–606. Bibcode:1986MNRAS.223..595M. doi:10.1093/mnras/223.3.595.
- "RV Crv". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- Abhyankar, K. D.; Parthasarathy, M.; Sanwal, N. B.; Sarma, M. B. K. (January 1974). "UBV photometry of RV CrV". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement. 13: 101. Bibcode:1974A&AS...13..101A.
- Buttery, Irene G. (1942). "Twenty-two new variable stars in MWF 10". Annals of Harvard College Observatory. 109: 25–26. Bibcode:1942AnHar.109...25B.
- Shaw, J. Scott; et al. (April 1996). "Near-Contact Binary Systems in the ROSAT All-Sky Survey". Astrophysical Journal. 461: 951. Bibcode:1996ApJ...461..951S. doi:10.1086/177116.
На других языках
- [en] RV Corvi
[ru] RV Ворона
RV Ворона (лат. RV Corvi, HD 109796) — тройная звезда в созвездии Ворона на расстоянии приблизительно 689 световых лет (около 211 парсек) от Солнца. Видимая звёздная величина звезды — от +9,16m до +8,6m[7]. Возраст звезды определён как около 1,465 млрд лет[8].Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии