astro.wikisort.org - Asteroid
(357439) 2004 BL86 is a bright sub-kilometer asteroid and binary system, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 300 meters (980 ft) in diameter. It was discovered on 30 January 2004 by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico.[3] Its 70-meter (200 ft) moon was discovered during the asteroid's close approach to the Earth in January 2015.[4][5]
 Goldstone radar image of 2004 BL86 and its minor-planet moon | |
| Discovery[1][2] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | LINEAR |
| Discovery site | Lincoln Lab's ETS |
| Discovery date | 30 January 2004 |
| Designations | |
MPC designation | (357439) 2004 BL86 |
Minor planet category | NEO · PHA · Apollo[1][3] |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 4 September 2017 (JD 2458000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 4,863 d (13.31 yr) |
| Aphelion | 2.1070 AU |
| Perihelion | 0.8974 AU |
Semi-major axis | 1.5022 AU |
| Eccentricity | 0.4026 |
Orbital period (sidereal) | 673 d (1.84 yr) |
Mean anomaly | 169.27° |
Mean motion | 0° 32m 7.08s / day |
| Inclination | 23.775° |
Longitude of ascending node | 126.69° |
Argument of perihelion | 311.45° |
| Known satellites | 1[4][5] |
| Earth MOID | 0.0092 AU (3.6 LD) |
| Physical characteristics | |
Mean diameter | 0.263±0.026 km[6] 0.290±0.030 km[7] 0.325±0.025 km[5][lower-alpha 1] |
Synodic rotation period | 2.620±0.001 h[6] 2.6205±0.0003 h[8] 2.637±0.024 h[7] |
Geometric albedo | 0.40[7] 0.40±0.08[6] |
Spectral type | V[7][9][10] |
Absolute magnitude (H) | 19.05[9] 19.3[1][7] 19.51±0.02[6] |
2015 Earth approach
On 26 January 2015 at 16:20 UTC, 2004 BL86 passed 1,199,600 km (745,400 mi), or 3.1 lunar distances, from Earth.[11] The asteroid briefly peaked around apparent magnitude 9 and was near the celestial equator.[12] The asteroid was visible in telescopes with objectives of 100 mm (4 in) or larger; high-end binoculars under a dark sky may also have worked.[13] Near closest approach the asteroid was moving about 2.5 degrees per hour (2.5 arcseconds per second).[12][14] The asteroid came to opposition (furthest elongation in the sky from the Sun) on 27 January 2015 at 04:37 UTC.[12] Around 5:00 UTC, the asteroid was near M44 (the Beehive Cluster).[14]
The 26 January 2015 approach of 3.1 lunar distances was the closest approach of 2004 BL86 for at least the next 200 years.[11][15] For comparison, 2015 TB145, about twice the size of 2004 BL86, passed 486,800 km (302,500 mi), or 1.3 lunar distances, from Earth on 31 October 2015.[16]
Satellite
A minor-planet moon, provisionally designated S/2015 (357439) 1, was first detected by ground-based telescopes by Joe Pollock and Petr Pravec.[8][17] Observations by the Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex and Green Bank Telescope confirmed that it is a binary asteroid with a secondary roughly 70 meters (200 ft) across.[5] The secondary is estimated to orbit at least 500 meters (1,600 ft) from the primary.[4] About 16% of asteroids over 200 meters (660 ft) in diameter are thought to be binaries.[5]
Numbering and naming
This minor planet was numbered on 27 March 2013 (M.P.C. 83151).[18] As of 2020, it has not been named.[3]
Gallery
 Animation of 2004 BL86's orbit
Animation of 2004 BL86's orbit
Sun · Earth · 2004 BL86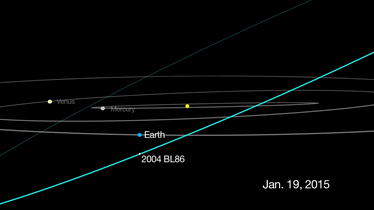 2004 BL86 safely passes Earth on 26 January 2015
2004 BL86 safely passes Earth on 26 January 2015 Trajectory of 2004 BL86 during Earth close approach
Trajectory of 2004 BL86 during Earth close approach- 2004 BL86 (star trail on left) near Xi Puppis
Notes
- Radar Team 2015a: diameter primary 0.325±0.025 km. Diameter secondary 0.070 km. The satellites discovery is credited to Pollock et al.[lower-alpha 2] Summary figures for (357439) 2004 BL86 at LCDB
References
- "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 357439 (2004 BL86)" (2017-05-24 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- "MPEC 2004-B80 : 2004 BL86". IAU Minor Planet Center. 31 January 2004. Retrieved 7 June 2014. (K04B86L)
- "357439 (2004 BL86)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 30 September 2020.
- Johnston, Wm. Robert (31 January 2015). "Asteroids with Satellites Database – (357439) 2004 BL86". Johnston's Archive. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- Agle, D. C. (26 January 2015). "Asteroid That Flew Past Earth Today Has Moon". NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- Reddy, Vishnu; et al. (September 2015). "The Physical Characterization of the Potentially Hazardous Asteroid 2004 BL86: A Fragment of a Differentiated Asteroid". The Astrophysical Journal. 811 (1): 10. arXiv:1509.07122. Bibcode:2015ApJ...811...65R. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/811/1/65. S2CID 119260041.
- Birlan, M.; et al. (September 2015). "Characterization of (357439) 2004 BL86 on its close approach to Earth in 2015". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 581: 7. Bibcode:2015A&A...581A...3B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201526460.
- Pollock, J.; Pravec, P.; Oey, J.; Reichart, D. E.; Haislip, J. B.; LaCluyze, A. P. (January 2015). "(357439) 2004 BL_86". Central Bureau Electronic Telegrams. 4063 (4063): 1. Bibcode:2015CBET.4063....1P.
- "LCDB Data for (357439)". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- Franco, Lorenzo (July 2015). "Low Resolution Visible Reflectance Spectrum for NEA (357439) 2004 BL86". The Minor Planet Bulletin. 42 (3): 186–187. Bibcode:2015MPBu...42..186F. ISSN 1052-8091.
- "JPL Close-Approach Data: 357439 (2004 BL86)" (last observation: 12 March 2013; arc: 9.11 years). NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 7 June 2014.
- "(357439) 2004BL86 Ephemerides for 25 January 2015 through 29 January 2015". NEODyS. Retrieved 7 June 2014.
- Musgrave, Ian (23 January 2015). "Seeing the Close Flyby of NEO 2004 BL86 26 - 27 January, 2015". Retrieved 28 January 2015.
- MacRobert, Alan (22 January 2015). "Mountain-size Asteroid Glides Past Earth". Sky & Telescope. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- Busch, Michael (7 February 2015). "Final post-flyby update..." Twitter.com. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- "JPL Close-Approach Data: 2015 TB145" (last observation: 1 November 2015; arc: 22 days). NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 2 December 2015.
- "Image Release: High-Def Radar Images of Near-Earth Asteroid". National Radio Astronomy Observatory. 30 January 2015. Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- "MPC/MPO/MPS Archive". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 29 November 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to (357439) 2004 BL86. |
- Asteroids with Satellites, Robert Johnston, johnstonsarchive.net
- PSI Scientists Study Surface Composition of Asteroid 2004 BL86 During Close Flyby of Earth, Planetary Science Institute, 27 January 2015
- Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB), query form (info Archived 16 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine)
- (357439) 2004 BL86 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- (357439) 2004 BL86 at ESA–space situational awareness
- (357439) 2004 BL86 at the JPL Small-Body Database
На других языках
[de] (357439) 2004 BL86
(357439) 2004 BL86 ist ein Asteroid von etwa 330 Metern Größe, dessen Bahn ihn am 26. Januar 2015 um 16:20 Uhr UTC bis auf einen Abstand von rund eine Million Kilometer an die Erde heranführte.[1][2] Er wurde am 30. Januar 2004 im Rahmen eines Projektes zur Himmelsüberwachung (LINEAR) entdeckt.[3]- [en] (357439) 2004 BL86
[ru] (357439) 2004 BL86
(357439) 2004 BL86 — околоземный астероид из группы Аполлонов, открытый LINEAR 30 января 2004 года[1]. По приблизительным оценкам размер астероида в диаметре составляет 325 метров.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии






