astro.wikisort.org - Comet
Comet Borrelly /bɒˈrɛli/ or Borrelly's Comet (official designation: 19P/Borrelly) is a periodic comet, which was visited by the spacecraft Deep Space 1 in 2001. The comet last came to perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) on February 1, 2022[1][8] and will next come to perihelion on December 11, 2028.[2]
 | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Alphonse Borrelly |
| Discovery date | December 28, 1904 |
| Designations | |
Alternative names | 1905 II; 1911 VIII; 1918 IV; 1925 VIII; 1932 IV; 1953 IV; 1960 V; 1967 VIII; 1974 VII; 1981 IV; 1987 XXXIII; 1994 XXX |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch 2022-08-09 (JD 2459800.5) | |
| Aphelion | 5.90 AU[1] |
| Perihelion | 1.306 AU[1] |
Semi-major axis | 3.61 AU |
| Eccentricity | 0.6377 |
Orbital period (sidereal) | 6.85 yr |
| Inclination | 29.30° |
Time of perihelion | 2028-Dec-11[2] February 1, 2022 (last)[1] |
| Earth MOID | 0.36 AU (54 million km) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 8×4×4 km[3] |
Mean radius | 2.4 km[4] |
| Mass | 2×1013 kg[5] |
Mean density | 0.3 g/cm3[6] |
| Albedo | 0.03[7] |
| Perihelion distance at recent epochs[1] | |||||||
| Epoch | Perihelion (AU) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2028 | 1.310[2] | ||||||
| 2022 | 1.306 | ||||||
| 2015 | 1.349 | ||||||
| 2008 | 1.355 | ||||||
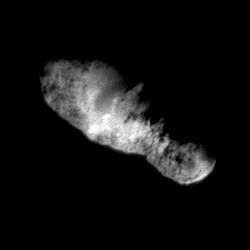
Deep Space 1 returned images of the comet's nucleus from 3400 kilometers away. At 45 meters per pixel, it was the highest resolution view ever seen of a comet.[9]
Discovery
The comet was discovered by Alphonse Borrelly during a routine search for comets at Marseilles, France on December 28, 1904.
Deep Space 1 flyby

Deep Space 1 · 9969 Braille · Earth · 19P/Borrelly
On September 21, 2001 the spacecraft Deep Space 1, which was launched to test new equipment in space, performed a flyby of Borrelly. It was steered toward the comet during the extended mission of the craft, and presented an unexpected bonus for the mission scientists. Despite the failure of a system that helped determine its orientation, Deep Space 1 managed to send back to Earth what were, at the time, the best images and other science data from a comet.

References
- MPC
- "Horizons Batch for 19P/Borrelly (90000304) on 2028-Dec-11" (Perihelion occurs when rdot flips from negative to positive). JPL Horizons. Retrieved 2022-06-15. (JPL#K223/24 Soln.date: 2022-Jun-08)
- Weaver, H. A.; Stern, S.A.; Parker, J. Wm. (2003). "Hubble Space Telescope STIS Observations of Comet 19P/BORRELLY during the Deep Space 1 Encounter". The Astronomical Journal. The American Astronomical Society. 126 (1): 444–451. Bibcode:2003AJ....126..444W. doi:10.1086/375752.
- "19P/Borrelly: Facts & Figures". Archived from the original on 2014-08-09. Retrieved 2014-08-08.
- Using the volume of an ellipsoid of 8x4x4km * a rubble pile density of 0.3 g/cm3 yields a mass (m=d*v) of 2.0E+13 kg.
- D. T. Britt; G. J. Consol-magno SJ; W. J. Merline (2006). "Small Body Density and Porosity: New Data, New Insights" (PDF). Lunar and Planetary Science XXXVII. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 December 2008. Retrieved 2008-12-16.
- Robert Roy Britt (2001-11-29). "Comet Borrelly Puzzle: Darkest Object in the Solar System". Space.com. Archived from the original on 22 January 2009. Retrieved 2008-12-16.
- Seiichi Yoshida (2021-04-03). "19P/Borrelly". Seiichi Yoshida's Comet Catalog. Retrieved 2022-06-15.
- Beatty, Kelly (25 June 2004). "Meet Comet Borrelly". Sky & Telescope. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
External links
- http://jcometobs.web.fc2.com/pcmtn/0019p.htm
- 19P – Gary W. Kronk's Cometography
- Elements and Ephemeris for 19P/Borrelly – Minor Planet Center
На других языках
[de] 19P/Borrelly
Der Komet Borrelly (offizielle Bezeichnung 19P/Borrelly) ist ein kurzperiodischer Komet, der am 22. September 2001 durch die NASA-Raumsonde Deep Space 1 erforscht wurde.- [en] 19P/Borrelly
[es] 19P/Borrelly
19P/Borrelly o cometa Borrelly es un cometa periódico que fue visitado por la nave Deep Space 1 en el 2001.[ru] 19P/Борелли
Комета Борелли (19P/Borrelly) — короткопериодическая комета из семейства Юпитера, которая была открыта 28 декабря 1904 года французским астрономом Альфонсом Борелли в Марсельской обсерватории, когда комета медленно двигалась по созвездию Кита. Она была описана как диффузный объект около до 2 ' угловых минут в поперечнике с центральной конденсацией. В 2001 году комета стала объектом исследования для космического зонда Deep Space 1. Комета обладает довольно коротким периодом обращения вокруг Солнца — чуть более 6,8 года.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии

