astro.wikisort.org - Star
V1298 Tauri is a young (23±4 Myr) weakly-lined T Tauri star[5] that is part of the Taurus-Auriga association in the Taurus Molecular Cloud. Alternatively it is part of a proposed moving group, called Group 29 that is slightly older.[6][7][3] The system has four transiting exoplanets, discovered with the Kepler space telescope in the K2 mission.[5] One of the planets was discovered in August 2019[3] and the other three were discovered in November 2019 by the same team.[5]
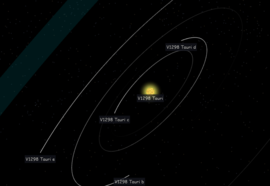 The planetary system V1298 Tauri Credit: Exoplanet Exploration Program and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA’s Astrophysics Division | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Taurus |
| Right ascension | 04h 05m 19.59121s[1] |
| Declination | +20° 09′ 25.5635″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 10.31 - 10.43[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K0-K1.5[3] |
| Variable type | Irregular[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 5.228 ± 0.131[1] mas/yr Dec.: -16.077 ± 0.048[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 9.2139 ± 0.0593 mas[1] |
| Distance | 354 ± 2 ly (108.5 ± 0.7 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.095+0.049 −0.047[4] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.33+0.04 −0.03[4] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.934 ± 0.044[3] L☉ |
| Temperature | 4970 ± 120[3] K |
| Rotation | 2.97+0.03 −0.04 d[4] |
| Age | 23 ± 4[3] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Stellar characteristics
![A light curve for V1298 Tauri, adapted from David et al. (2019)[3]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f5/V1298TauLightCurve.png/220px-V1298TauLightCurve.png)
V1298 Tauri has a spectral type of K0 - K1.5 and it has a mass of about 1.1 M☉. The star appears in x-rays from ROSAT data and it does show strong lithium absorption lines, both signatures of youth and therefore it was a proposed member of Taurus-Auriga. On the other hand it does not show signs of accretion and it lacks infrared excess. Instead it shows H-alpha in absorption.[3]
The brightness of V1298 Tauri varies in an unpredictable way between a maximum visual magnitude of 10.31 and a minimum of 10.54.[2] The light curve of the star shows quasi-periodic variability that was interpreted as stellar rotation and starspots. The light curve also showed several flares.[3]
Based on Gaia DR2 data this star is part of a co-moving pair, together with HD 284154.[6]
Planetary system
V1298 Tauri has four confirmed planets of which planets c, d and b are near a 1:2:3 resonance (with periods of 8.25, 12.40 and 24.14 days). Planet e only shows a single transit in the K2 light curve and has a period larger than 36 days. Planet e might be in a low-order resonance (of 2:3, 3:5, 1:2, or 1:3) with planet b. The system is very young and might be a precursor of a compact multiplanet system. The 2:3 resonance suggests that some close-in planets may either form in resonances or evolve into them on timescales of less than 10 Myr. The planets in the system have a size between Neptune and Saturn. Only planet b has a size similar to Jupiter.[5]
Models predict that the planets have a minimum core mass of 5 MEarth and are surrounded by a thick envelope that make up 20% of their mass. The total mass of planet c and d was predicted to be 2 - 28 MEarth and the total mass of planet d and b was predicted to be 9 - 120 MEarth.[5] In a follow-up paper the mass of V1298 Tauri b was constrained to <2.2 MJ.[8] The planet c was suspected to be shedding mass due to intense irradiation by the host star, but hydrogen tail existence was refuted by 2021.[9]
Orbits of the planets b and c are nearly coplanar and planet c is not inclined to the equatorial plane of the star, misalignment equals to 2+12
−4 degrees.[10]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c | — | 0.0825 ± 0.0013 | 8.24958 ± 0.00072 | <0.43 | 88.49+0.92 −0.72° |
0.499+0.032 −0.029 RJ |
| d | — | 0.1083 ± 0.0017 | 12.4032 ± 0.0015 | <0.21 | 89.04+0.65 −0.73° |
0.572+0.040 −0.035 RJ |
| b | <2.2 MJ | 0.1688 ± 0.0026 | 24.1396 ± 0.0018 | <0.29 | 89.00+0.46 −0.24° |
0.916+0.052 −0.047 RJ |
| e | — | 0.308+0.182 −0.066 |
50.29±6.62[11] | <0.57 | 89.40+0.26 −0.18° |
0.89±0.04[11] RJ |
See also
- List of nearby stellar associations and moving groups
- List of exoplanets discovered in 2019
- Kepler-223 - the first confirmed system with four exoplanets in resonance
- K2-138 - a system with five exoplanets in a 3:2 resonance chain
References
- Gaia Collaboration (2018-08-01). "Gaia Data Release 2 - Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616: A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. ISSN 0004-6361. S2CID 49211658.
- Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1: B/gcvs. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- David, Trevor J.; Cody, Ann Marie; Hedges, Christina L.; Mamajek, Eric E.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A.; Ciardi, David R.; Beichman, Charles A.; Petigura, Erik A.; Fulton, Benjamin J.; Isaacson, Howard T.; Howard, Andrew W. (August 2019). "A Warm Jupiter-sized Planet Transiting the Pre-main-sequence Star V1298 Tau". The Astronomical Journal. 158 (2): 79. arXiv:1902.09670. Bibcode:2019AJ....158...79D. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab290f. ISSN 0004-6256. S2CID 119003936.
- Feinstein, Adina D.; David, Trevor J.; Montet, Benjamin T.; Foreman-Mackey, Daniel; Livingston, John H.; Mann, Andrew W. (2022). "V1298 Tau with TESS: Updated Ephemerides, Radii, and Period Constraints from a Second Transit of V1298 Tau E". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 925 (1): L2. arXiv:2111.08660. Bibcode:2022ApJ...925L...2F. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac4745. S2CID 244130016.
- David, Trevor J.; Petigura, Erik A.; Luger, Rodrigo; Foreman-Mackey, Daniel; Livingston, John H.; Mamajek, Eric E.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2019-10-29). "Four Newborn Planets Transiting the Young Solar Analog V1298 Tau". The Astrophysical Journal. 885 (1): L12. arXiv:1910.04563. Bibcode:2019ApJ...885L..12D. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab4c99. ISSN 2041-8213. S2CID 204008446.
- Oh, Semyeong; Price-Whelan, Adrian M.; Hogg, David W.; Morton, Timothy D.; Spergel, David N. (June 2017). "Comoving Stars in Gaia DR1: An Abundance of Very Wide Separation Comoving Pairs". The Astronomical Journal. 153 (6): 257. arXiv:1612.02440. Bibcode:2017AJ....153..257O. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa6ffd. ISSN 0004-6256. S2CID 119351439.
- Luhman, K. L. (December 2018). "The Stellar Membership of the Taurus Star-forming Region". The Astronomical Journal. 156 (6): 271. arXiv:1811.01359. Bibcode:2018AJ....156..271L. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aae831. ISSN 0004-6256. S2CID 119471553.
- Beichman, Charles; Hirano, Teruyuki; David, Trevor J.; Kotani, Takayuki; Hillenbrand, Lynne A.; Vasisht, Gautam; Ciardi, David R.; Harakawa, Hiroki; Kudo, Tomoyuki; Omiya, Masashi; Kuzuhara, Masayuki (June 2019). "A Mass Limit for the Young Transiting Planet V1298 Tau b". Research Notes of the AAS. 3 (6): 89. Bibcode:2019RNAAS...3...89B. doi:10.3847/2515-5172/ab2c9d. ISSN 2515-5172.
- H-Alpha Variability of V1298 Tau c, 2021, arXiv:2108.08851
- Zodiacal Exoplanets in Time (ZEIT) XIII: Planet Orbits and Atmospheres in the V1298 Tau System, a Keystone in Studies of Early Planetary Evolution, 2021, arXiv:2110.10689
- V1298 Tau with TESS: Updated Ephemerides, Radii, and Period Constraints from a Second Transit of V1298 Tau e, 2021, arXiv:2111.08660
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии