astro.wikisort.org - Galaxy
A1689-zD1 is a galaxy in the Virgo constellation. It was a candidate for the most distant and therefore earliest-observed galaxy discovered as of February 2008[update], based on a photometric redshift.[1][2]
| A1689-zD1 | |
|---|---|
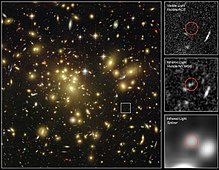 Location of A1689-zD1 in infrared and visible light by Hubble Space Telescope and Spitzer Space Telescope | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Virgo |
| Right ascension | 13h 11m 29.9s |
| Declination | −01° 19′ 19″ |
| Redshift | 7.6 |
| Helio radial velocity | 2,278,423 km/s |
| Galactocentric velocity | 2,278,351 +/- 3 km/s |
| Distance | 13 billion light-years (light travel distance) 30 billion light-years (present proper distance) |
| Group or cluster | Abell 1689 |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 25.3 |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | Dwarf |
| Mass | 1.7×109 M☉ |
| Size | ~3,000 ly (diameter) |
| Apparent size (V) | 0.0008 x 0.0008 |
| Other designations | |
| BBF2008 A1689-zD1 | |
If the redshift, z~7.6,[3] is correct, it would explain why the galaxy's faint light reaches us at infrared wavelengths. It could only be observed with Hubble Space Telescope's Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) and the Spitzer Space Telescope's Infrared Array Camera exploiting the natural phenomenon of gravitational lensing: the galaxy cluster Abell 1689, which lies between Earth and A1689-zD1, at a distance of 2.2 billion light-years from us, functions as a natural "magnifying glass" for the light from the far more distant galaxy which lies directly behind it, at 700 million years after the Big Bang, as seen from Earth.[1]
See also
- IOK-1
- UDFy-38135539
- List of the most distant astronomical objects
References
- "Astronomers Eye Ultra-Young, Bright Galaxy in Early Universe". NASA. 2008-02-12. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- "Astronomers Uncover One of the Youngest and Brightest Galaxies in the Early Universe". Space Telescope Science Institute Baltimore, Md. / nasa.gov. 2008-02-12. Archived from the original on 17 February 2008. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- "heic0805: Hubble finds strong contender for galaxy distance record". ESA/Hubble. 2008-02-12. Archived from the original on 8 March 2008. Retrieved 2008-04-04.
На других языках
[de] A1689-zD1
A1689-zD1 ist mit einer Rotverschiebung von z = ~7.6 eine der am weitesten entfernten bekannten Galaxien überhaupt. Die Entdeckung mit Hilfe des Hubble-Weltraumteleskops wurde im Februar 2008 bekannt gegeben.[1][2]- [en] A1689-zD1
[es] A1689-zD1
A1689-zD1 es una de las galaxias más antiguas, y la más lejana descubierta desde febrero de 2008[1] hasta el descubrimiento de UDFy-38135539 en 2010.[2][ru] A1689-zD1
A1689-zD1 — галактика в скоплении галактик в созвездии Девы. Является одной из наиболее далёких наблюдаемых галактик (на момент наблюдения, февраль 2008 года) на основе данных о фотометрическом красном смещении[2][3].Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии